DWDM Fiber Optic Transmission

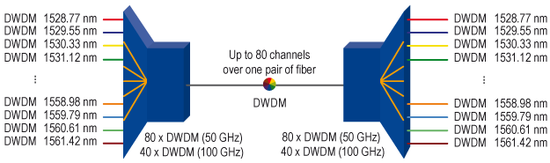
DWDM stands for “Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing” and allows per definition up to 40/80 DWDM wavelengths over one pair of fiber.
DWDM highlights:
- Up to 90 DWDM wavelength over one pair of fiber
- DWDM channel spacing 0.8 nm (100 GHz grid) or 0.4 nm (50 GHz grid)
- Distances over 1,000 km can be achieved with the use of optical amplifier
- DWDM wavelength: 1528 nm (channel 61) to 1563 nm (channel 17)
DWDM principle
The functionality of DWDM resembles to the one of CWDM. Unlike to CWDM technology, the channel spacing for DWDM is 0.8/0.4 nm (100 GHz/50 GHz grid).
This small channel spacing allows to transmit simultaneously much more information. Currently a restriction on wavelengths between 1530 nm and 1625 nm exists which corresponds to the C and L band.
In this connection DWDM wavelengths from DWDM technology is more expensive compared to CWDM caused by the need of more sophisticated transceivers.
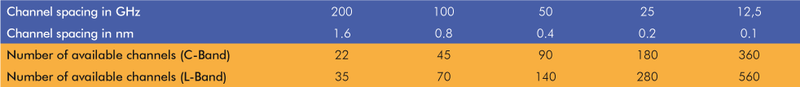
Theoretically available DWDM channels in the C- and L-band depending on the channel spacing.
Technical Details:
- ITU-T G.694.1
- C-Band λ: 1530 nm – 1565 nm max. 360 channels (12,5 GHz Grid)
- L-Band λ: 1565 nm – 1625 nm max. 560 channels (12,5 GHz Grid)
